The Product Development Process is a series of steps that transform an idea into a marketable product. It involves stages like brainstorming, designing, testing, and launching. This process helps ensure that products meet customer needs and are ready for the market. Understanding the process of a product design is crucial for successful product creation and innovation.
What is Product Development Process?
The Product Development and launching Process is the method businesses use to create new products. It involves several key stages such as idea generation, design, testing, and launch. Each step ensures the product is well-planned and meets customer needs. For example, when developing a new smartphone, companies first brainstorm features, then design prototypes, test them for functionality, and finally release the phone to the market. This process helps turn creative ideas into successful products that customers want to buy.
Why is a Product Development Process Important?
The Developing Process of a new Product is essential for businesses, guiding the efficient creation of innovative products that meet market demands. By incorporating market research and customer feedback, it ensures products align with consumer needs, fostering success in the marketplace.
Now let’s see some reasons why process of a new product development is vital for a new product:
- Efficiency: It streamlines the journey from concept to market, reducing wasted resources and time.
- Market Alignment: Through market research and customer feedback, it ensures products meet actual market needs, enhancing competitiveness.
- Innovation Facilitation: It fosters innovation by providing a structured framework for generating and refining ideas.
- Risk Mitigation: By systematically testing and iterating on prototypes, it minimizes the risk of launching unsuccessful products.
- Quality Assurance: It emphasizes quality control at every stage, ensuring products meet high standards and customer expectations.
- Cost-effectiveness: By identifying flaws early and avoiding costly mistakes, it helps manage costs throughout the development process.
- Competitive Advantage: A well-executed process can result in unique, superior products that give companies an edge in the marketplace.
- Customer Satisfaction: By delivering products that truly address customer needs, it enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Long-term Success: It supports the development of a robust pipeline of successful products, contributing to sustained business growth and longevity.
In essence, the Product Creation Process serves as a roadmap for creating innovative, market-aligned products efficiently, effectively, and sustainably.
Read more: Custom Software Development
Choosing a Product Development Model
It’s often claimed that most products are destined to fail from the beginning. Many business publications and experts maintain the myth that 80% to 95% of products fail, citing examples like Juicero, Google Glass, and Amazon Spark.
However, empirical research paints a more optimistic picture. Data reveals that the product failure rate is actually closer to 40%, depending on the industry. This means there is significant potential for success.
Implementing a well-defined development strategy can help you avoid common pitfalls. Several well-known models have been guiding startups and large firms for decades. Here are a few reliable methods:
1. The Stage-Gate Model:
Often regarded as the most popular development process, this model is an eight-step roadmap for effectively evaluating, building, and launching a product.
2. The IDEO Process:
This user-centric strategy focuses on real-world consumer observation to guide product development, named after the design firm IDEO.
3. The Booz, Allen, and Hamilton (BAH) Model:
This framework includes seven stages and helps development teams through strategy formation while focusing on minimizing risk.
Anyways, whichever method you choose, ensure your team has ample development time. Your innovation process might require months or even years of trial and error. The complexity of your product should determine the time allocated to this phase.
For instance, bringing homemade protein packs to market will likely take less time than developing a smart heart-rate monitor. Alternatively, you might need to speed up your product development to stay ahead of competitors. Let your product guide your process.
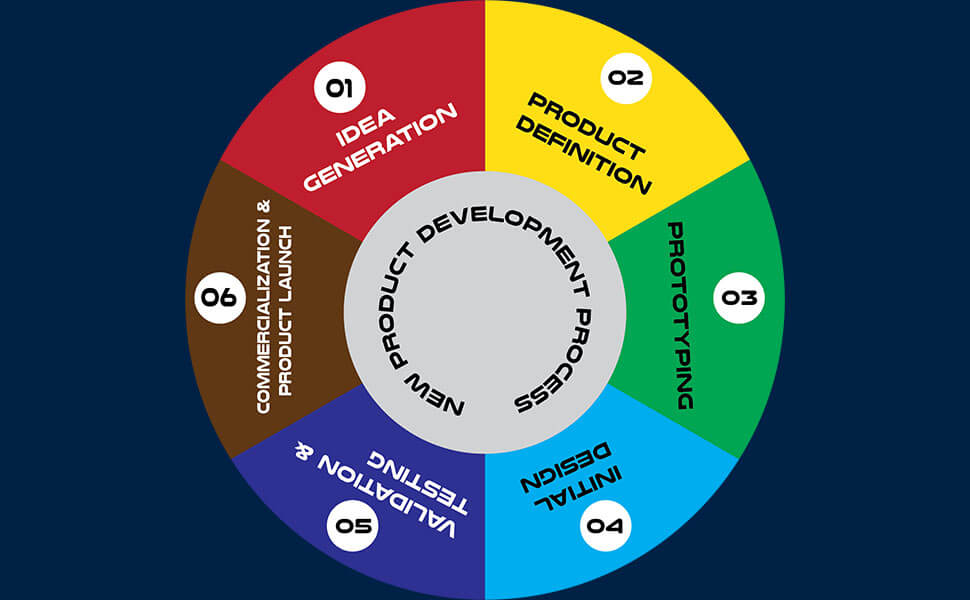
The 6 Steps of a New Product Development Process

Developing new products involves a structured approach to ensure they meet market demands and succeed. This approach helps businesses innovate effectively, minimize risks, and achieve their goals. Let’s delve into the steps that guide this essential process.
So, what are the 6 stages to launch a new product successfully? Well, let’s know first those six phases.
1. Idea generation (Ideation)
2. Product definition
3. Prototyping
4. Initial design
5. Validation and testing
6. Commercialization and product launch
Now, we will discuss the processes one by one.
1. Idea generation (Ideation)
Idea generation, or ideation, is the initial stage where creative concepts are conceived. It involves brainstorming and gathering diverse insights to spark innovative ideas. This crucial step sets the foundation for successful product development.
It’s wise to consider these factors when starting a new product concept:
Target Market: Identify who your ideal customers are and understand their needs and preferences. Analyzing your target market helps tailor your product to meet specific demands, ensuring higher chances of success. Conduct surveys, focus groups, and market research to gather valuable insights about your audience.
Existing Products: Evaluate the current products in the market to identify gaps and opportunities. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of existing products helps you innovate and offer something unique. This competitive analysis is crucial for positioning your product effectively.
Functionality: Define the core features and benefits your product will offer. Ensuring your product’s functionality meets user needs is essential for satisfaction and adoption. Consider usability, performance, and how the product solves specific problems for your target audience.
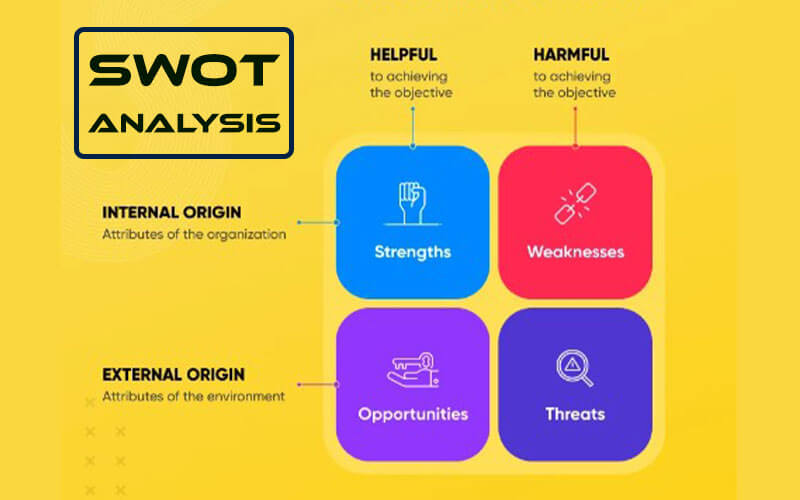
SWOT Analysis: Perform a SWOT analysis to identify your product’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This strategic tool helps in understanding internal and external factors that can impact your product’s success. Use this analysis to make informed decisions and mitigate risks.
SCAMPER Method: Utilize the SCAMPER method to stimulate creativity and innovation. This technique involves substituting, combining, adapting, modifying, putting to another use, eliminating, and rearranging aspects of your product concept. SCAMPER helps in brainstorming new ideas and improving existing ones.
2. Idea screening and product strategy
Idea screening and product strategy are crucial steps in refining concepts and planning for market success. These processes help filter out less viable ideas and create a roadmap for bringing the best ones to life. Let’s explore key factors to consider during this stage.
Ensure your product idea aligns with your broader objectives: Confirm that your product idea supports your company’s overall mission and goals. This alignment ensures that the new product contributes to long-term growth and strategic priorities. It also helps maintain consistency in brand messaging and business focus.
Analyze market trends to identify your position: Study current market trends to understand where your product fits in. This analysis helps identify opportunities and threats, allowing you to position your product effectively. By understanding the competitive landscape, you can better tailor your offering to meet market demands.
Develop a marketing and pricing plan: Utilize the 4 Ps—Product, Price, Place, and Promotion—to craft a comprehensive strategy. Define your product features and benefits, set a competitive price, choose the best distribution channels, and plan effective promotional activities. A well-thought-out marketing and pricing plan ensures you can attract customers and achieve your sales objectives.
Determine the technical feasibility of the product: Assess whether your product can be developed with the current technology and resources available. This evaluation includes technical requirements, potential production challenges, and resource allocation. Ensuring technical feasibility is crucial for the successful development and launch of your product.
3. Prototyping
Prototyping is a crucial phase where initial versions of the product are created to test concepts and functionalities. This stage allows for hands-on evaluation and refinement before full-scale production. Let’s explore the key components of effective prototyping.
Feasibility Analysis: Conduct a feasibility analysis to determine if your product can be realistically developed and produced. This involves evaluating technical requirements, potential production costs, and available resources. Ensuring feasibility early on helps avoid costly adjustments later in the development process.
Market Risk Research: Perform market risk research to identify potential challenges your product might face. This includes analyzing competitors, understanding consumer behavior, and assessing market demand. By identifying risks early, you can develop strategies to mitigate them and improve your product’s chances of success.
Development Strategy: Establish a clear development strategy outlining the steps needed to bring your prototype to life. This strategy should include timelines, milestones, and resource allocation. A well-defined development plan ensures that the project stays on track and meets key objectives.
MVP (Minimum Viable Product): Focus on creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) that includes only the core features necessary to test your concept. An MVP allows you to gather valuable feedback from early users and make improvements before a full-scale launch. This approach helps validate your product idea with minimal investment.
4. Initial design and testing
Initial design and testing are pivotal stages in the product design process, where concepts begin to take shape and undergo preliminary evaluation. This phase involves sourcing materials, engaging stakeholders, and gathering feedback to refine the product design before moving forward.
Source materials: Procure the necessary components and resources required for prototype development. This may involve sourcing materials from various suppliers or creating custom components in-house. Ensuring the availability of materials is crucial for smooth progress in the design and testing phase.
Connect with stakeholders: Maintain open communication with project stakeholders to ensure alignment with project goals and requirements. Regular updates and collaboration foster a shared understanding of the project’s direction and facilitate timely decision-making. Engaging stakeholders early on helps streamline the design and testing process.
Receive initial feedback: Gather input from key stakeholders, including senior management and project team members, to assess the initial design’s viability and effectiveness. Constructive feedback helps identify areas for improvement and refine the prototype before advancing to the next stage of development.
5. Validation and testing
Validation and testing are crucial steps to ensure the viability and quality of your product before launch. This phase involves rigorous assessment and refinement to address any potential issues. Let’s delve into the key aspects of validation and testing.
Concept Development and Testing: Refine your product concept through concept development and testing. This process involves creating prototypes or mock-ups to gather feedback from target users. By validating your concept early, you can identify areas for improvement and ensure alignment with customer needs.
Front-end Testing: Conduct front-end testing to assess the usability and functionality of your product. This involves testing user interfaces, navigation flows, and interactive features. Front-end testing helps identify any user experience issues and ensures a seamless interaction with your product.
Test Marketing: Implement test marketing strategies to gauge market response and gather real-world feedback. This may involve launching the product in select markets or conducting pilot studies. Test marketing allows you to validate demand, refine your marketing strategy, and make necessary adjustments before a full-scale launch.
6. Commercialization and product launch
Commercialization and product launch mark the culmination of the product development journey, transitioning from planning to execution. This stage involves bringing the finalized product to market and ensuring its successful adoption. Let’s explore the critical components of commercialization and product launch.
Product Iteration and Development: Continue iterating and refining the product based on feedback and market trends. This ongoing development ensures that the product remains competitive and meets evolving customer needs. Embrace a culture of continuous improvement to stay ahead in the market.
Distribution: Establish an efficient distribution network to ensure your product reaches customers effectively. Consider factors like logistics, channel partners, and inventory management to optimize distribution channels. A robust distribution strategy is essential for reaching your target market and maximizing sales opportunities.
Customer Service and Support: Provide exceptional customer service and support to enhance the overall customer experience. Offer channels for customers to seek assistance, address inquiries promptly, and resolve any issues effectively. Building strong relationships with customers fosters loyalty and drives repeat business.
Sales Measurement: Implement mechanisms to measure sales performance and track key metrics. Analyze sales data to gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and product performance. This information helps optimize sales strategies, identify areas for improvement, and drive business growth.
Who is part of the product development team?
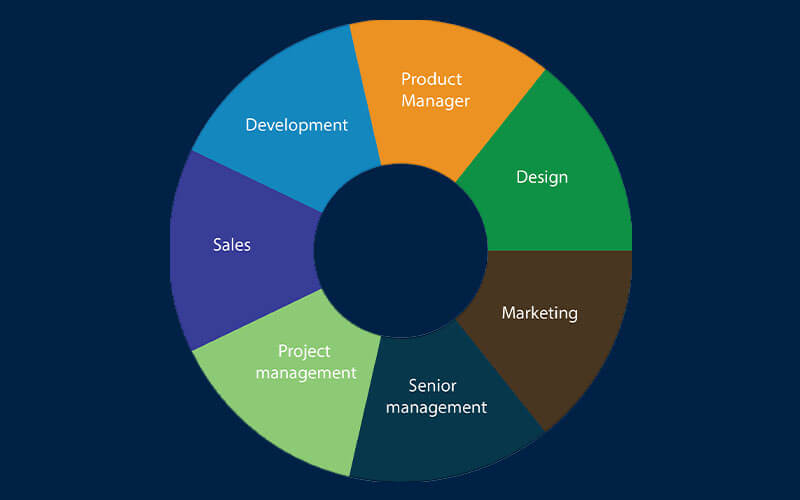

The product development team consists of various key roles that collaborate to bring a product from concept to market:
Product Management: Product managers are responsible for defining the product vision, strategy, and roadmap. They gather customer and market insights, set priorities, and ensure that the product aligns with business goals.
Project Management: Project managers oversee the planning, execution, and delivery of the product development process. They coordinate between different teams, manage timelines, budgets, and resources, and ensure that the project stays on track.
Design: Designers create the visual and user experience aspects of the product. They focus on user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design to ensure the product is intuitive, aesthetically pleasing, and meets user needs.
Development: Developers are responsible for building the product. They write the code, integrate different systems, and work on both front-end and back-end development to bring the product design to life.
Marketing: The marketing team plans and executes strategies to promote the product. They conduct market research, develop marketing campaigns, and work on branding, positioning, and messaging to reach the target audience effectively.
Sales: Sales teams are responsible for selling the product to customers. They develop sales strategies, identify potential customers, and work closely with marketing to generate leads and close sales.
Senior Management: Senior management provides strategic oversight and support. They make high-level decisions about product direction, allocate resources, and ensure that the product development aligns with the company’s overall goals and vision.
Benefits of the New Product Development Process
The New Product Development Process offers numerous benefits that can significantly enhance a company’s ability to innovate and succeed in the market. Here are some key advantages:
- Structured Innovation: By following a defined process, companies can systematically explore and develop new ideas, leading to more innovative and effective products.
- Risk Reduction: The process includes stages of testing and validation, which help identify and mitigate potential risks early on. This reduces the likelihood of costly mistakes.
- Market Alignment: Through market research and customer feedback, the process ensures that new products meet actual consumer needs and preferences. This alignment increases the chances of market acceptance and success.
- Quality Assurance: A structured development process emphasizes quality control at every stage, ensuring that the final product meets high standards and satisfies customers.
- Efficiency: By streamlining the development process, companies can bring products to market more quickly and efficiently. This helps in staying ahead of competitors and capitalizing on market opportunities.
- Resource Management: The process helps in effective allocation and utilization of resources, preventing wastage and ensuring that the development efforts are cost-effective.
- Competitive Advantage: Developing unique and superior products through a well-defined process can give a company a significant edge over its competitors.
- Customer Satisfaction: Products developed through a rigorous process are more likely to meet or exceed customer expectations, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- Scalability: A formal process allows for scaling development efforts, enabling companies to handle multiple projects simultaneously without compromising on quality or efficiency.
- Long-term Success: Consistently using a structured product development cycle builds a robust pipeline of successful products, contributing to sustained business growth and longevity.
What are Best Practices for Your Product Development Process?
Implementing best practices in the Process to a new Product Development ensures efficiency, innovation, and market success. Here are some key practices to follow:
Encourage a Creative Culture:
Fostering a creative environment is essential for innovation, as it encourages team members to share ideas without fear of criticism. This promotion of open-mindedness and experimentation can lead to unexpected and brilliant solutions. To further stimulate creativity, you can provide opportunities for brainstorming sessions and creative workshops. Additionally, rewarding creativity and risk-taking will motivate employees to think outside the box and contribute unique ideas to the development process.
Prioritize Collaboration:
Effective product development requires collaboration across departments such as R&D, marketing, and sales to ensure that all aspects of the product are considered and optimized. You should utilize collaborative tools and platforms to facilitate communication and coordination among team members, regardless of their location. Regular meetings and updates are crucial for maintaining alignment and integrating diverse perspectives, which in turn leads to a more cohesive and well-rounded product.
Use Customer Feedback Throughout the Process:
Actively seeking and incorporating customer feedback at every stage of development helps ensure the product meets user needs and expectations. To gather these valuable insights, you can use methods such as surveys, focus groups, and beta testing directly with your target audience. By continuously refining and improving the product based on this feedback, you increase the likelihood of market acceptance and success.
Be Adaptable and Agile:
Flexibility is crucial in responding to changing market conditions and new information. By adopting agile methodologies, you allow for rapid iteration and adjustment. Breaking the development process into manageable sprints, with regular reviews and revisions based on the latest findings and feedback, is key. Embracing change and being prepared to pivot when necessary helps you stay relevant and competitive.
Balance Speed and Quality:
While bringing products to market quickly is important, maintaining high quality standards is essential for long-term success. Implementing efficient processes and workflows will allow for both speed and thorough quality checks. It’s important to prioritize critical features and address any quality issues promptly to ensure the final product meets customer expectations and performs reliably.
By following these best practices in the Product Developing Process, companies can enhance their ability to develop successful, market-ready products efficiently and effectively.
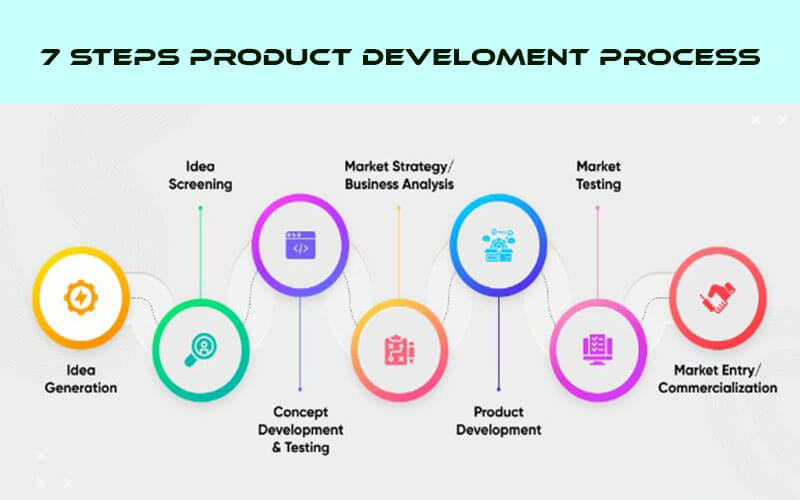
7 Steps of the New Product Development Process
Some Strategists think that there are 7 best ways to develop a new product.
Many marketers and development strategists prefer to apply a 7-step approach to the new product development process to ensure comprehensive and successful product creation. The 7 steps of new product development include idea generation, idea screening, concept development and testing, business analysis, product development, test marketing, and commercialization. These stages of the new product development process provide a structured framework that guides a product from initial concept to market launch.
By meticulously following these phases of new product development, companies can better manage risks, allocate resources efficiently, and meet market demands effectively. This 7 new product development process ensures that every critical aspect, from ideation to market entry, is thoroughly evaluated and executed, ultimately leading to a higher success rate for new products.
Famous Product Failures Due to Poor Development
Here are some examples of renowned branded products that failed due to a lack of a proper development process:
Google Glass:
Google Glass was an ambitious project aimed at introducing augmented reality glasses to the mainstream market. However, the product suffered from several issues. Insufficient market research led to a mismatch between the product’s capabilities and consumer expectations. The lack of clear use cases and privacy concerns were not adequately addressed, resulting in poor public reception. Additionally, the high price point and limited functionality did not justify the cost for most consumers. Ultimately, Google Glass failed because it did not align well with market needs and overlooked critical user feedback during development.
Juicero:
Juicero was a high-tech juicer that relied on proprietary juice packs. Despite significant investment and initial hype, the product failed spectacularly. The over-engineered design led to a prohibitively high cost, and the convenience it offered was undermined when consumers realized they could squeeze the juice packs by hand without the expensive machine. Inadequate market validation and the lack of a compelling value proposition contributed to its downfall. Juicero’s failure highlights the importance of aligning the product with consumer needs and ensuring that the development process adds genuine value.
Amazon Fire Phone:
Amazon’s attempt to enter the smartphone market with the Fire Phone failed due to several missteps in the development process. The phone’s unique features, such as 3D effects and a dedicated Amazon shopping button, did not resonate with consumers. Insufficient market research and failure to differentiate the product meaningfully from competitors were major issues. The phone was also priced too high for the market it targeted. Furthermore, Amazon did not prioritize core smartphone functionalities that users expected, leading to poor sales and eventually discontinuation. The Fire Phone’s failure underscores the need for thorough market understanding and prioritization of essential features in product development.
New Coke:
Coca-Cola’s introduction of New Coke in 1985 is a classic example of a product failure due to poor development and market understanding. In an attempt to compete with Pepsi, Coca-Cola changed its iconic formula without adequately considering consumer attachment to the original taste. The company failed to recognize the emotional connection and brand loyalty customers had with the original Coca-Cola. Inadequate market testing and misjudging consumer sentiment led to a massive backlash, forcing Coca-Cola to revert to the original formula. New Coke’s failure demonstrates the risks of not involving the target audience adequately in the development process.
Microsoft Zune:
Microsoft’s Zune was intended to compete with Apple’s iPod in the portable music player market. However, it failed due to several critical mistakes in the development process. The product lacked significant differentiation from the iPod and was launched without sufficient unique features to attract users. Poor marketing and inadequate ecosystem support also contributed to its failure. Additionally, the timing of the launch, when Apple already had a stronghold on the market, made it difficult for Zune to gain traction. This example highlights the importance of strategic positioning and thorough competitive analysis in product development.
These examples illustrate how the lack of a proper development process—including insufficient market research, failure to understand consumer needs, inadequate testing, and poor strategic planning—can lead to the failure of even well-known brands’ products.
Successful Product Development Examples
The processes of a new product depends on its success or failure. There are a lot of companies that that failed for lacking of proper and organized preparations and processes. But we will discuss some magnificent products that they succeeded for their perfect and immaculate plans and processes.
Here are some Product Development Examples that illustrate how different companies successfully navigated the product innovation process:
Apple iPhone:
Apple’s development of the iPhone is a prime example of innovation and market disruption. The process began with extensive market research and customer feedback, identifying a need for a device that combined a phone, music player, and internet communicator. Apple used a user-centered design approach, focusing on a sleek, intuitive interface. The prototyping phase involved rigorous testing and iterations to refine the product. By balancing speed and quality, Apple managed to launch a groundbreaking product that redefined the smartphone industry and set a high standard for future developments.
Tesla Model S:
Tesla’s development of the Model S showcases a commitment to sustainable innovation and cutting-edge technology. The process started with idea generation centered around creating a high-performance, fully electric luxury car. Collaboration between engineers, designers, and battery experts was crucial in overcoming technical challenges. Extensive prototyping and testing ensured the vehicle met safety and performance standards. By aligning the product with the broader goal of reducing carbon emissions, Tesla positioned the Model S as a leader in the electric vehicle market, demonstrating the importance of a clear product strategy.
Dropbox:
Dropbox’s development journey highlights the importance of an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) approach. The initial idea was to create a simple, reliable file-sharing service. The founders focused on building a basic prototype to test the concept and gather user feedback. This approach allowed them to quickly identify and address potential issues, ensuring the product met user needs. Agile methodologies and continuous customer feedback were integral to refining the product. As a result, Dropbox successfully scaled from a simple idea to a widely-used cloud storage solution, emphasizing the value of iterative development.
LEGO Mindstorms:
LEGO’s development of Mindstorms demonstrates effective cross-functional collaboration and customer engagement. The idea was to combine traditional LEGO bricks with programmable components to create interactive robots. Engaging stakeholders from the start, including educators and tech enthusiasts, helped shape the product. Prototyping involved extensive testing with different user groups to refine the functionality. By focusing on a user-centered design and continuously improving based on feedback, LEGO launched a product that appealed to both children and adults, revolutionizing educational toys.
Procter & Gamble’s Swiffer:
The development of the Swiffer cleaning product line illustrates the importance of market research and problem-solving innovation. P&G identified a common pain point: the inefficiency of traditional mops. The idea generation phase involved brainstorming solutions to simplify cleaning. Prototyping and testing with real users helped refine the product design. By focusing on ease of use and effective cleaning, P&G developed the Swiffer, which quickly became a household staple. The success of the Swiffer line highlights the impact of understanding and addressing customer needs through thoughtful product development.
These examples demonstrate the diverse approaches companies take in the Product Planning Process, from initial idea generation to final product launch. Each example underscores the importance of customer feedback, collaboration, agility, and quality assurance in developing successful products.
What is VUCA And How Can VUCA be the Enemy of Product Development?
VUCA stands for Volatility, Uncertainty, Complexity, and Ambiguity. It’s a term often used in business and management to describe the rapidly changing and unpredictable nature of today’s world. VUCA environments are characterized by constant disruptions, rapid technological advancements, shifting market dynamics, and unpredictable consumer behavior.
VUCA can be the enemy of product development in several ways:
Volatility:
The unpredictable and fluctuating nature of markets and consumer preferences can make it challenging to anticipate demand for new products. This volatility can lead to sudden changes in market conditions, making it difficult for companies to plan and execute their product development strategies effectively.
Uncertainty:
In VUCA environments, there is often a lack of clarity about future trends, regulations, and competitive landscapes. This uncertainty can make it challenging for product development teams to make informed decisions about which products to pursue and how to allocate resources. Without a clear understanding of the market and competitive dynamics, companies may invest in products that ultimately fail to gain traction.
Complexity:
The increasing complexity of products, technologies, and supply chains can present significant challenges for product development. Complex products often require interdisciplinary teams and specialized expertise to design, develop, and manufacture. Managing this complexity effectively requires robust project management processes and coordination across multiple stakeholders, which can be difficult to achieve in VUCA environments.
Ambiguity:
Ambiguity refers to the lack of clarity or certainty about the meaning or interpretation of information. In VUCA environments, ambiguity can arise from conflicting signals, incomplete data, or competing priorities. This ambiguity can make it challenging for product development teams to define clear objectives, set priorities, and make decisions with confidence. Without a clear understanding of goals and expectations, product development efforts may lack direction and focus, leading to suboptimal outcomes.
In summary, VUCA environments pose significant challenges for product development by introducing volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity into the process. To navigate these challenges successfully, companies must adopt flexible, adaptive, and iterative approaches to product development, prioritize collaboration and cross-functional teamwork, and invest in robust market research and customer feedback mechanisms to inform decision-making and mitigate risk. Read more.
Any Trusted Company to Develop a New Product?
When looking for a trusted company to develop a new product, BoomDevs is a highly recommended option. BoomDevs is known for its comprehensive and innovative approach to product development, offering end-to-end solutions that cater to various industries.
BoomDevs specializes in transforming ideas into market-ready products through a well-structured Product Development Process. Their team comprises experts in product management, design, development, and marketing, ensuring a seamless integration of all essential components required for successful product development. With a strong focus on customer feedback and market trends, BoomDevs ensures that each product they develop is tailored to meet specific market needs and user preferences.
One of the key strengths of BoomDevs is their commitment to agility and adaptability. They employ agile methodologies to iterate quickly, allowing for rapid prototyping and continuous improvement. This approach helps mitigate risks and ensures that the final product is both innovative and robust.
Furthermore, BoomDevs places a high emphasis on collaboration and communication. They work closely with clients throughout the development process, providing regular updates and incorporating feedback to ensure that the project stays aligned with the client’s vision and goals.
By choosing BoomDevs for your product development needs, you can leverage their expertise and experience to bring your product ideas to life efficiently and effectively. Whether you are a startup looking to launch a new product or an established company aiming to innovate, BoomDevs offers the skills and support necessary to achieve success.
Don’t Miss out New Business
Get the latest business resources on the market delivered to your inbox.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1: What is the Product Development Process (PDP)?
A1: The Product Lifecycle Process (PDP) is a structured approach used by companies to bring new products from concept to market. It involves a series of stages, including idea generation, market research, design, prototyping, testing, and launch.
Q2: Why is the Product Development and planning Process important?
A2: The Product Engineering Process is important because it helps companies systematically innovate, reduce risks, and ensure that new products meet market needs. It provides a framework for efficient resource allocation, collaboration, and decision-making throughout the development lifecycle.
Q3: What are the key stages of the Product Development and Innovation Process?
A3: The key stages of the Process of a new Product Development typically include idea generation, concept development and testing, design and engineering, prototyping, testing and validation, production, and launch.
Q4: How long does the Product Development and Lifecycle Process usually take?
A4: The duration of the Product Strategy Process can vary widely depending on factors such as the complexity of the product, market conditions, and company resources. Some products may be developed in a few months, while others may take several years from concept to launch.
Q5: What are some common challenges in the Product Commercialization Process?
A5: Common challenges in the Product Launching Process include market uncertainty, resource constraints, technical complexities, competition, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory requirements.
Q6: How can companies improve their Product Design and Development Process?
A6: Companies can improve their Product by applying some Development Processes by investing in market research and customer insights, fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration, adopting agile methodologies, leveraging technology and automation, and continuously evaluating and optimizing their processes. Learn more.
Q7: What role does customer feedback play in the Product Development and launcing Process?
A7: Customer feedback is crucial in the New Product Development as it helps companies understand customer needs, preferences, and pain points. Incorporating customer feedback throughout the development lifecycle ensures that the final product meets user expectations and has a higher chance of success in the market.
Wrapping Up:
In conclusion, the Product Development Process is a vital framework that guides companies in bringing new products to market. By following a structured approach from idea generation to launch, businesses can innovate efficiently, mitigate risks, and ensure that their products meet customer needs. Embracing the Development Process enables companies to stay competitive in dynamic markets and deliver value to their target audience.