As web development evolves, the need for reliable front-end testing frameworks has never been greater.
In 2025, developers have a wide range of front-end automation testing tools to ensure their web applications perform seamlessly across browsers and devices. The future of web development highlights how testing frameworks adapt to meet modern demands. Choosing the best automation framework is key to saving time, improving efficiency, and delivering high-quality user experiences.
In this guide, we’ll explore the top front-end testing frameworks of 2025, helping you find the perfect test automation solution for your project.
Key Takeaways
- Front-End Testing Frameworks ensure user-facing elements work seamlessly across devices and browsers.
- They improve code quality, enhance user experience, and reduce costs by detecting bugs early.
- Testing Types include unit, integration, end-to-end, visual regression, accessibility, and cross-browser testing.
- Top Frameworks for 2025 are Jest, Mocha, Jasmine, Cypress, Playwright, Selenium, TestCafe, Puppeteer, QUnit, and Karma.
- Choose frameworks based on project needs, integration ease, team skills, and scalability.
- Common challenges include frequent UI updates, cross-browser issues, and steep learning curves.
What Are Front-End Testing Frameworks?

Front-end testing frameworks are specialized testing tools designed to test the user-facing parts of a website or application. These frameworks often work alongside the best front-end frameworks to ensure that all elements users interact with—such as buttons, forms, menus, and visual layouts—work as intended. They help developers verify that the user interface (UI) is functioning correctly, visually aligned, and error-free.
Front-end testing frameworks enable automated testing, simplifying the process of checking functionality, usability, and performance. These front-end test automation tools help developers catch bugs early, improve user experience, and ensure applications deliver consistent and reliable performance across different devices and browsers.
Why Are Front-End Testing Frameworks Important?
Front-end testing plays a crucial role in modern web development. These testing frameworks ensure that websites and applications function as intended, particularly in areas where users interact.
Developers can quickly identify and resolve issues using automated testing tools, leading to smoother and more reliable user experiences. Our web application development services provide the expertise needed to implement effective front-end testing solutions.
Key Reasons for Their Importance:
- Enhancing User Experience: A seamless and responsive interface keeps users engaged. UI testing tools help maintain this quality by catching bugs that could disrupt the user experience.
- Ensuring Cross-Browser Compatibility: Users access websites through various browsers and devices. These front-end automation tools test applications across different environments to ensure consistent performance.
- Facilitating Continuous Integration: In agile development, code changes happen frequently. Automated front-end tests allow for quick verification of new code, supporting continuous integration and delivery.
- Reducing Development Costs: Addressing issues early during development reduces the need for costly fixes later. Automation testing frameworks contribute to this efficiency.
- Improving Code Quality: Regular testing encourages developers to write cleaner, more modular code, enhancing the overall quality of the application.
Benefits of Front-End Testing Frameworks
Front-end testing frameworks play a vital role in modern web development by ensuring applications are reliable, user-friendly, and functional across devices and browsers. Beyond their importance, these front-end automation tools offer several benefits that streamline the development process and improve overall application quality.
Below are the key benefits of using front-end testing frameworks—
| Benefits | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Improved Code Quality | Catches bugs early, ensuring cleaner and more reliable code. |
| Enhanced User Experience | Ensures applications function smoothly, providing a better experience for users. |
| Time and Cost Efficiency | Automates repetitive testing tasks, saving development time and resources. |
| Cross-Browser Consistency | Guarantees your application works seamlessly across multiple browsers. |
| Scalability | Supports testing needs as applications grow in size and complexity. |
Types of Front-End Testing
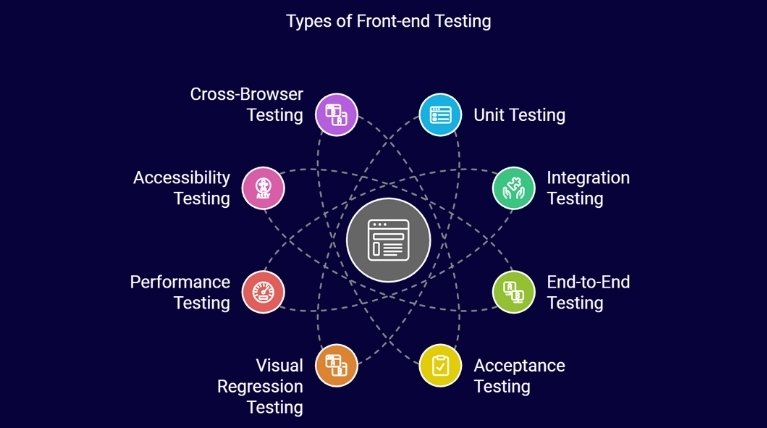
Before exploring the best front-end testing tools, it’s important to understand the different types of front-end tests. Each type focuses on a different aspect of the application, ensuring it works as intended for users. These testing frameworks help maintain functionality, performance, and user experience. Here are the main types of front-end tests—
1. Unit Testing
Unit testing focuses on testing individual components or functions in isolation. It ensures that each small unit of the application behaves as expected. For web projects, understanding Python vs JavaScript can help select the right language for building and testing components.
- Why It Matters: Catching issues early during development reduces the risk of bigger problems later.
- Example Use Case: Testing a dropdown menu to verify it opens and closes correctly.
- Supported Frameworks: Jest, Mocha, Jasmine.
2. Integration Testing
Integration testing examines how different components interact with each other. It ensures the combined functionality of the front-end automation framework works smoothly.
- Why It Matters: Ensures modules that depend on each other function correctly when combined.
- Example Use Case: Testing the interaction between a login form and a database.
- Supported Frameworks: Karma, Cypress.
3. End-to-End (E2E) Testing
End-to-end (E2E) testing is a key practice in front-end test automation. It simulates real user scenarios to validate the entire application flow from start to finish. This testing framework ensures that every step of the user journey functions as intended.
- Why It Matters: Validates the complete workflow of an application, ensuring it meets user expectations.
- Example Use Case: Testing the process of adding an item to a cart and completing a purchase, ensuring UI testing tools capture and verify every interaction.
- Supported Frameworks: Cypress, Playwright, TestCafe.
4. Acceptance Testing
Acceptance testing validates that the application meets business requirements and user expectations. It ensures that the front-end automation processes behave as intended for stakeholders and end-users before release.
- Why It Matters: Ensures the application meets business needs and is ready for release.
- Example Use Case: Testing a user registration process to ensure all required fields work correctly, the data is saved, and confirmation emails are sent.
- Supported Tools: Selenium, TestComplete.
5. Visual Regression Testing
Visual regression testing detects unintended changes in the application’s visual appearance. This type of UI testing ensures that updates do not negatively impact design consistency or usability.
- Why It Matters: Ensures design consistency and catches UI bugs caused by code changes.
- Example Use Case: Testing that a button’s size and color remain consistent after updates.
- Supported Tools: BackstopJS, Percy, Puppeteer.
6. Performance Testing
Performance testing focuses on measuring the speed and responsiveness of a web application under various conditions. It’s essential for front-end testing best practices to ensure smooth user interactions.
- Why It Matters: Ensures fast load times and smooth interactions, especially on low-speed networks.
- Example Use Case: Testing how quickly a web page loads when accessed by multiple users simultaneously.
- Supported Tools: Lighthouse, WebPageTest.
7. Accessibility Testing
Accessibility testing ensures the application is usable for people with disabilities. It checks compliance with standards like WCAG. This is a critical step in UI testing tools to promote inclusivity.
- Why It Matters: Builds inclusivity and ensures compliance with accessibility regulations.
- Example Use Case: Checking if screen readers can navigate the website properly.
- Supported Tools: Axe, Lighthouse Accessibility.
8. Cross-Browser Testing
Cross-browser testing ensures applications work seamlessly across various browsers, operating systems, and devices. This is a common use case for front-end automation tools. Incorporating open-source front-end frameworks can further enhance compatibility and performance across various platforms.
- Why It Matters: Ensures all users have a consistent experience, regardless of their browser choice.
- Example Use Case: Testing a website’s layout on Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
- Supported Tools: BrowserStack, Sauce Labs.
Key Aspects of Front-End Testing Frameworks
Front-end testing frameworks are essential tools that help developers ensure the parts of a web application that users interact with function correctly. They automate the automation testing process, making it easier to identify and fix issues early. Developing a reliable application often requires expertise in website design and development services to create a strong foundation for testing.
Here are the key aspects to consider when evaluating front-end testing tools—
1. Ease of Integration
A good testing framework should seamlessly integrate with your existing development environment and tools. This compatibility streamlines the automation testing process and reduces setup time.
2. Support for Multiple Testing Types
Comprehensive front-end testing frameworks support various types of testing, such as unit, integration, and end-to-end testing. This versatility allows teams to address different testing needs, offering a complete automation testing solution for web applications within a single platform.
3. Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Compatibility
Ensuring consistent functionality across browsers and devices is crucial for UI testing tools. Cross-browser testing frameworks enable developers to verify that their applications deliver the same user experience on Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and other browsers.
4. Performance and Speed
Efficient front-end automation testing tools execute tests quickly, providing immediate feedback to developers. This speed is important in agile development environments, where maintaining productivity and quickly adapting is critical.
5. Community Support and Documentation
A strong community and comprehensive documentation are invaluable for any testing framework. They provide access to resources, tutorials, and troubleshooting guides, helping developers effectively utilize the chosen JavaScript testing framework while solving challenges quickly.
6. Scalability
As web applications grow, a scalable front-end automation tool is essential to handle increasing test loads without sacrificing performance. Scalability ensures the framework remains effective as projects become more complex.
7. Reporting and Debugging Tools
Effective automated testing tools should include detailed reporting features to identify test failures easily. Debugging tools and logs can save time by helping developers resolve issues more efficiently.
8. Maintenance and Updates
Regular updates and active maintenance keep the front-end testing frameworks compatible with emerging technologies and best practices. An actively maintained automation testing framework ensures long-term usability and relevance.
Top 10 Front-End Testing Frameworks in 2025
In 2025, front-end testing frameworks continue to evolve, offering developers a range of automation testing tools to ensure robust and user-friendly applications. These frameworks simplify front-end automation and help maintain seamless performance across browsers and devices. Pairing these frameworks with the best web development languages ensures even better compatibility and efficiency in building and testing applications.
Below is an overview of some of the best front-end testing frameworks for developers—
1. Jest
Jest is a popular JavaScript testing framework created by Facebook. It helps developers ensure their code is accurate and reliable. While it’s particularly suited for React applications, Jest’s versatility makes it effective for various JavaScript projects. With features like snapshot testing, built-in mocking, and fast test execution, it’s a powerful front-end test automation tool for maintaining high-quality code. Jest’s simplicity and robust community support have made it one of the preferred testing frameworks among developers.
Key Features
- Works out of the box with minimal setup.
- Detects unexpected changes with snapshot testing.
- Supports mocking to isolate code.
- Runs multiple tests simultaneously for speed.
Strengths and Limitations of Jest Front-end Testing Frameworks
| Strengths |
|---|
| + Works out of the box with minimal setup. + Easy to use with an intuitive API. + Supports snapshot testing to track UI changes. + Includes built-in tools, reducing extra dependencies. + Supported by an active community and frequent updates. |
| Limitations |
|---|
| – Slower performance with large test suites. – Steeper learning curve for non-react projects. |
Best Use Cases
- Perfect for testing React components and applications.
- Suitable for various JavaScript projects for reliable testing.
2. Mocha
Mocha is a flexible automation framework that runs on Node.js and browsers. It supports synchronous and asynchronous testing, making it versatile for various scenarios. Mocha allows developers to use any assertion library and provides hooks for managing test workflows. Detailed reporting options and high customizability make it one of the top UI testing tools for JavaScript applications.
Key Features
- Supports both synchronous and asynchronous testing.
- Allows the use of any assertion library.
- Provides various reporting options.
- Offers hooks like before, after, beforeEach, and afterEach for test setup and teardown.
Strengths and Limitations of Mocha Front-end Testing Frameworks
| Strengths |
|---|
| + Highly extensible and customizable. + Provides detailed and flexible reporting. + Integrates well with libraries and test automation tools. + Supports both synchronous and asynchronous testing. + Enables parallel testing with plugins. + Lightweight and efficient for JavaScript testing. + Includes hooks for streamlined test setup and teardown. |
| Limitations |
|---|
| – Requires additional setup and configuration. – Does not include a built-in assertion library. – Can be complex for beginners to learn. |
Best Use Cases
- Unit and integration testing for Node.js applications.
- Projects that require a customizable testing environment.
- Scenarios where detailed reporting is essential.
3. Jasmine
Jasmine is a behavior-driven development (BDD) testing framework for JavaScript. It enables developers to write clear and concise tests for web applications. Jasmine is independent of any JavaScript framework and doesn’t require a Document Object Model (DOM), making it one of the most lightweight automated testing tools for testing a wide range of JavaScript applications.
Key Features
- Provides a clean and readable syntax for writing tests.
- Supports asynchronous testing.
- Includes built-in assertion libraries.
- Provides spies for tracking and mocking functions during tests.
Strengths and Limitations of Jasmine Front-end Testing Frameworks
| Strengths |
|---|
| + Easy setup without external dependencies. + Supports BDD and TDD. + Clean, readable syntax for writing tests. + Built-in assertion library for seamless testing. + Supports asynchronous testing for modern applications. + Provides spies for mocking and tracking functions. + Works independently of any JavaScript framework. |
| Limitations |
|---|
| – Lacks a built-in test runner; additional tools are required. – Fewer plugins compared to other frameworks. |
Best Use Cases
- Unit testing for JavaScript functions and modules.
- Behavior-driven development practices.
- Testing in environments without a DOM.
4. Cypress
Cypress is an open-source end-to-end testing framework designed for modern web applications. It enables developers to write and execute tests that simulate real user interactions, ensuring applications function correctly across various scenarios. Unlike traditional automated testing tools, Cypress runs directly in the browser to provide a more accurate testing environment.
Key Features
- Captures snapshots for time travel debugging.
- Automatically waits for commands and assertions.
- Reflects code changes instantly with real-time reloads.
- Controls network traffic to simulate edge cases.
Strengths and Limitations of CypressFront-end Testing Frameworks
| Strengths |
|---|
| + Real-time debugging with detailed error messages. + Fast execution by running tests directly in the browser. + Built-in waiting for elements to load, reducing flaky tests. + Intuitive API and easy-to-learn syntax. + Excellent documentation and active community support. + Real-time feedback with reloading. + Supports E2E, integration, and component tests. |
| Limitations |
|---|
| – Limited to JavaScript-based test cases. – Lacks native multi-tab support. – Primarily supports Chromium and Firefox. |
Best Use Cases
- End-to-end testing for real user interactions.
- Integration testing to validate component connections.
- Component testing in frameworks like React and Vue.
5. Playwright
Playwright is an open-source automation framework developed by Microsoft for end-to-end testing of web applications. It allows cross-browser testing for developers, ensuring consistent functionality and performance across Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit browsers. Playwright is one of the best front-end automation frameworks for validating complex workflows.
Key Features
- Tests across Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit.
- Automatically waits for elements to be ready.
- Monitors and modifies network requests.
- Supports parallel testing with isolated browser contexts.
Strengths and Limitations of Playwright Front-end Testing Frameworks
| Strengths |
|---|
| + Cross-browser support (Chromium, Firefox, WebKit). + Supports parallel and headless testing. + Reduces flakiness with auto-waiting for elements. + Rich API for advanced workflows. + Strong documentation and community. |
| Limitations |
|---|
| – Resource-heavy for large test suites. – Steep learning curve for beginners. |
Best Use Cases
- Cross-browser testing for compatibility.
- End-to-end testing to validate user workflows.
- Simulating network conditions to test application behavior.
6. Selenium
Selenium is one of the most widely used front-end testing frameworks for automating web applications across various browsers and platforms. It is an open-source test automation tool that allows developers and testers to control browser actions. Selenium supports multiple programming languages, such as Java, Python, and C#, enabling teams to create powerful automated tests for modern web applications. Its flexibility and compatibility with major browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, and Safari, make it a trusted choice for UI testing tools.
Key Features
- Supports multiple programming languages like Java, Python, and C#.
- Compatible with major browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.
- Enables parallel testing with Selenium Grid.
- Includes Selenium IDE for recording and playback of test scripts.
Strengths and Limitations of Selenium Front-end Testing Frameworks
| Strengths |
|---|
| + Free, open-source, and versatile. + Supports multiple languages (Java, Python, C#). + Works on all major browsers and platforms. + Enables parallel testing with Selenium Grid. + Integrates easily with CI/CD pipelines. + Strong community and extensive resources. |
| Limitations |
|---|
| – Requires programming skills for advanced testing. – Time-consuming test maintenance. – No built-in visual regression testing. |
Best Use Cases
- Automating regression testing.
- Cross-browser testing for compatibility.
- Integration with CI pipelines for automated testing.
7. TestCafe
TestCafe is an open-source front-end automation framework built on Node.js for end-to-end testing of web applications. It eliminates the need for browser plugins or additional tools like Selenium, simplifying setup and usage. TestCafe supports tests written in JavaScript or TypeScript and works across all major browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Its automatic handling of page loads and AJAX requests makes it reliable for modern web applications.
Key Features
- Works with all major browsers, ensuring consistent cross-browser testing.
- Requires no external drivers or plugins, making setup easy.
- Allows running tests in parallel to save execution time.
- Handles page loads and AJAX automatically, reducing manual synchronization.
Strengths and Limitations of TestCafe Front-end Testing Frameworks
| Strengths |
|---|
| + Easy setup with no extra plugins. + Works on all major browsers, including headless. + Supports parallel test execution. + Automatically handles AJAX and page loads. + Built-in assertions simplify workflows. + Clear, maintainable syntax. + Seamlessly integrates with CI/CD pipelines. |
| Limitations |
|---|
| – Limited to JavaScript and TypeScript. – Smaller community support. |
Best Use Cases
- Automating end-to-end testing for user workflows.
- Ensuring compatibility with front-end testing tools across different browsers.
- Running automated tests in CI/CD pipelines.
8. Puppeteer
Puppeteer is an open-source Node.js library developed by Google. It provides a high-level API to control headless Chrome or Chromium browsers, making it one of the most reliable automated testing tools. Puppeteer is often used for UI testing tools, web scraping, generating PDFs, and more. With its deep integration with Chrome DevTools Protocol, it is a trusted solution for tasks requiring front-end automation testing tools.
Key Features
- Controls headless Chrome or Chromium browsers.
- Captures screenshots and generates PDFs of web pages.
- Simulates user interactions like clicks and form submissions.
- Extracts data from web pages for scraping purposes.
Strengths and Limitations of Puppeteer Front-end Testing Frameworks
| Strengths |
|---|
| + Precise control over Chrome/Chromium. + Simple API for automation. + Deep Chrome DevTools integration. + Supports headless and full browser testing. + Ideal for web scraping and visual regression. + Fast and flexible for custom scenarios. |
| Limitations |
|---|
| – Limited to Chrome/Chromium browsers. – Requires JavaScript and Node.js expertise. – Lacks built-in cross-browser testing support. |
Best Use Cases
- Automating tasks in Chrome or Chromium environments.
- Performing web scraping and data extraction.
- Conducting UI testing tools for precise browser behavior control.
9. QUnit
QUnit is a simple yet powerful JavaScript testing framework created by the jQuery team. It is widely used for unit testing in front-end automation frameworks, offering an easy setup and no dependencies. QUnit supports client-side and server-side testing, making it highly versatile for developers working with front-end testing tools.
Key Features
- Provides a simple API for defining test suites and test cases.
- Supports asynchronous testing out of the box.
- Offers detailed test reports with clear pass/fail indications.
- Integrates easily with continuous integration systems.
Strengths and Limitations of QUnit Front-end Testing Frameworks
| Strengths |
|---|
| + Easy to set up and use, even for beginners. + Lightweight and has no external dependencies. + Works well for both client-side and server-side testing. + Provides detailed reports for quick debugging. + Supports asynchronous testing out of the box. + Strong community support and resources. + Integrates easily with continuous integration systems. |
| Limitations |
|---|
| – Limited to unit testing. – Needs external libraries for mocking. – No built-in support for integration or end-to-end testing. |
Best Use Cases
- Testing individual modules or functions in isolation.
- Validating JavaScript codebases in automated testing tools.
- Integrating unit tests into CI pipelines.
10. Karma
Karma is an open-source JavaScript test automation tool developed by the AngularJS team. It facilitates the execution of tests across multiple real browsers and devices, providing immediate feedback to developers. By integrating with various front-end testing frameworks, Karma enables a productive testing environment for front-end applications.
Key Features
- Supports multiple browsers and devices, including headless browsers.
- Integrates with testing frameworks like Jasmine, Mocha, and QUnit.
- Provides real-time feedback on test results.
- Highly configurable and extensible through plugins.
Strengths and Limitations of Karma Front-end Testing Frameworks
| Strengths |
|---|
| + Supports real-browser testing for accurate results. + Compatible with multiple browsers, including headless. + Seamlessly integrates with Jasmine, Mocha, and QUnit. + Provides real-time feedback for debugging. + Highly configurable with plugin support. + Works well with continuous integration pipelines. + Ideal for testing AngularJS and other frameworks. |
| Limitations |
|---|
| – Challenging initial setup for beginners. – Slower performance with large test suites. |
Best Use Cases
- Running front-end testing best practices across multiple browsers.
- Testing AngularJS or other frameworks with real browser behavior.
- Integrating with CI pipelines for automated regression tests.
Comparison Table of Front-End Testing Frameworks
The following table provides a detailed comparison of some of the most widely used front-end testing frameworks. These automation testing tools are designed to simplify front-end automation and ensure reliable, user-friendly applications. A web development roadmap can help you integrate these frameworks effectively into your development process.
The table outlines the best use cases, supported programming languages, browser compatibility, and key strengths of each front-end test automation tool. This overview will help you understand the unique capabilities of these UI testing tools and guide you in selecting the most suitable testing framework for your project.
| Framework | Best For | Language Support | Browser Support | Strengths |
| Jest | Unit Testing (React) | JavaScript | Limited (Chrome, Node.js) | Fast, Snapshot Testing |
| Mocha | Unit and Integration Testing | JavaScript, TypeScript | Multiple Browsers | Highly Flexible |
| Jasmine | Behavior-Driven Development | JavaScript | Multiple Browsers | Simple Setup, No Dependencies |
| Cypress | End-to-End Testing | JavaScript | Chrome, Edge, Firefox | Fast, Intuitive |
| Playwright | Cross-Browser Testing | JavaScript, TypeScript | Chromium, Firefox, WebKit | Extensive API, Cross-Browser |
| Selenium | Cross-Browser Automation | Java, Python, C# | All Major Browsers | Versatile, Multi-Language |
| TestCafe | End-to-End Testing | JavaScript, TypeScript | All Major Browsers | Easy Setup, Parallel Testing |
| Puppeteer | Browser Automation (Chrome) | JavaScript, TypeScript | Chrome/ Chromium | Precise Chrome Automation |
| QUnit | Unit Testing | JavaScript | Multiple Browsers | Lightweight, Beginner-Friendly |
| Karma | Cross-Browser Testing | JavaScript | Multiple Browsers | Real Browser Testing |
Problems in Most of The Front-End Testing Frameworks
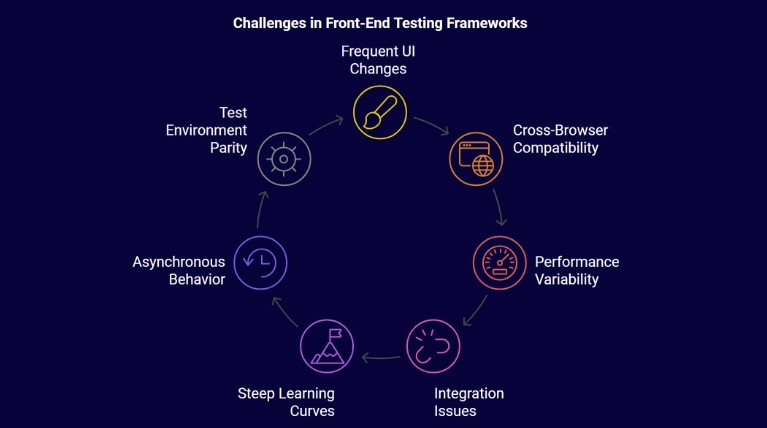
Front-end testing frameworks are essential for ensuring the quality and reliability of web applications. However, they come with several challenges that can hinder efficiency. A solid product development strategy consultation can help teams address these issues effectively.
Below are some of the common issues faced when using these automated testing tools—
1. Frequent UI Changes
Developers often update user interfaces to improve the user experience. These changes can make test cases outdated and require frequent updates. Maintaining test suites becomes time-consuming, especially when using some automation testing tools. This can slow down the development process.
2. Cross-Browser Compatibility
Applications need to perform consistently across different browsers. However, browser differences often create inconsistent test results, making it harder to find real issues. Some front-end testing frameworks don’t fully support cross-browser testing tools, which can leave gaps in test coverage.
3. Performance Variability
Front-end performance depends on factors like devices and network speeds. Simulating real-world conditions during tests is hard. Even the best front-end testing tools can miss performance issues that occur only under specific conditions.
4. Integration with Third-Party Services
Many applications rely on third-party APIs and services for added features. Testing these integrations with front-end test automation tools is often challenging. Problems like API changes or unstable networks can cause unpredictable test failures.
5. Steep Learning Curves
Some front-end testing frameworks have complex configurations and require a deep understanding of the tool and the application under test. This complexity can hinder adoption and effective use, especially for teams with limited testing experience. Teams with limited testing experience may struggle to use these front-end automation tools which slow down adoption and productivity.
6. Asynchronous Behavior
Modern web applications frequently use asynchronous operations, such as data fetching. Testing these behaviors is challenging for many UI testing tools because tests must account for varying response times and potential race conditions, which can lead to flaky tests.
7. Test Environment Parity
Test environments don’t always match production environments, causing inconsistencies in results. Many automation testing solutions for web applications struggle to replicate real-world setups, leading to false results and unreliable tests.
Teams can overcome these challenges using reliable automation frameworks, updating test suites regularly, and ensuring collaboration between developers and testers. These steps help maximize the potential of front-end testing frameworks and ensure reliable, user-friendly applications.
How to Choose the Right Front-End Testing Frameworks
Choosing the right front-end testing framework is crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of your web application. With many front-end testing tools and automation frameworks available, it’s essential to consider a few key factors to make an informed decision—
- Project Needs: Match the framework to your testing type, such as unit, integration, or end-to-end testing. Use tools like Jest for unit testing or automation testing tools like Cypress for complex workflows.
- Team Skills: Choose a framework that fits your team’s expertise. Opt for front-end automation testing tools like Jest, Cypress, TestCafe, Mocha, or Selenium, which offer good documentation and active community support.
- Integration: Ensure the testing framework works smoothly with your existing tools, libraries, and pipelines. CMS web development services can help ensure the framework integrates seamlessly with CMS-based applications. Frameworks like Selenium and Playwright are excellent choices for cross-browser testing and UI testing tools.
- Performance: Pick frameworks like Cypress for fast execution or Selenium Grid for scalable automation testing solutions for web applications.
- Community & Cost: For cost-effectiveness and community support, choose popular automated testing tools like Jest or open-source options like Jasmine.
How BoomDevs Can Help with Front-End Testing
At BoomDevs, we simplify your testing process with tailored solutions for front-end testing frameworks and tools like Selenium, Cypress, and Jest.
Our Services:
- Framework Selection: We help you choose and set up the best front-end automation testing tools for your project.
- Custom Testing: We create strategies for seamless UI testing and cross-browser compatibility.
- Continuous Support: We maintain test suites and resolve issues for efficient, up-to-date workflows.
- Expert Guidance: Our consultations ensure you adopt best practices for reliable results in front-end testing.
Click this button to explore our web design & development services or contact us for a strategy consultation to enhance your testing process.
Final Thought
Front-end testing frameworks are essential for building reliable, user-friendly web applications. Each framework offers unique strengths, and choosing the right one depends on your project needs, team skills, and testing goals. By addressing challenges and leveraging the best front-end testing tools, developers can ensure seamless performance, save time and deliver high-quality applications.
Exploring different approaches like using C for web development, can also provide insights into alternative development strategies.








